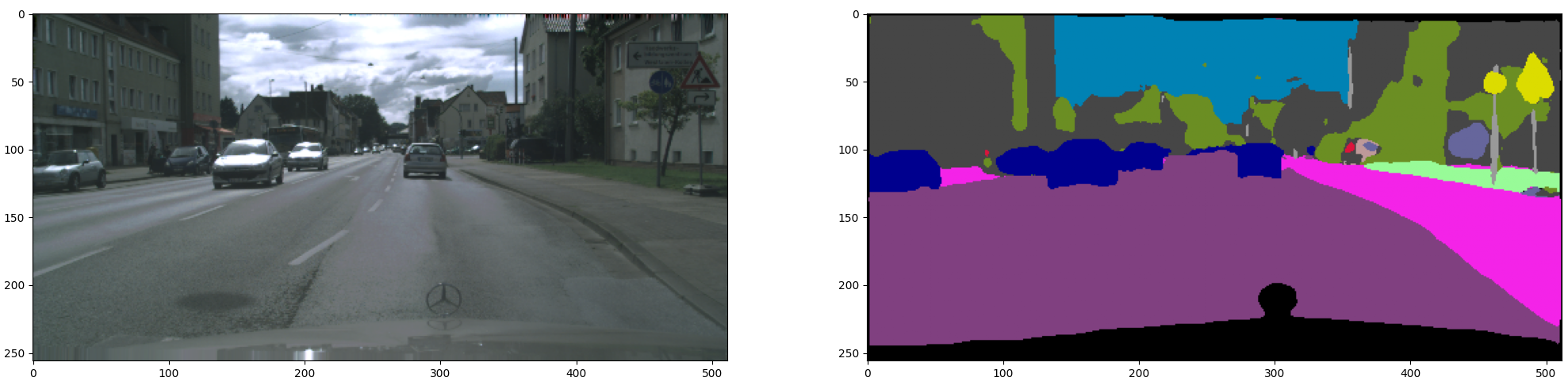
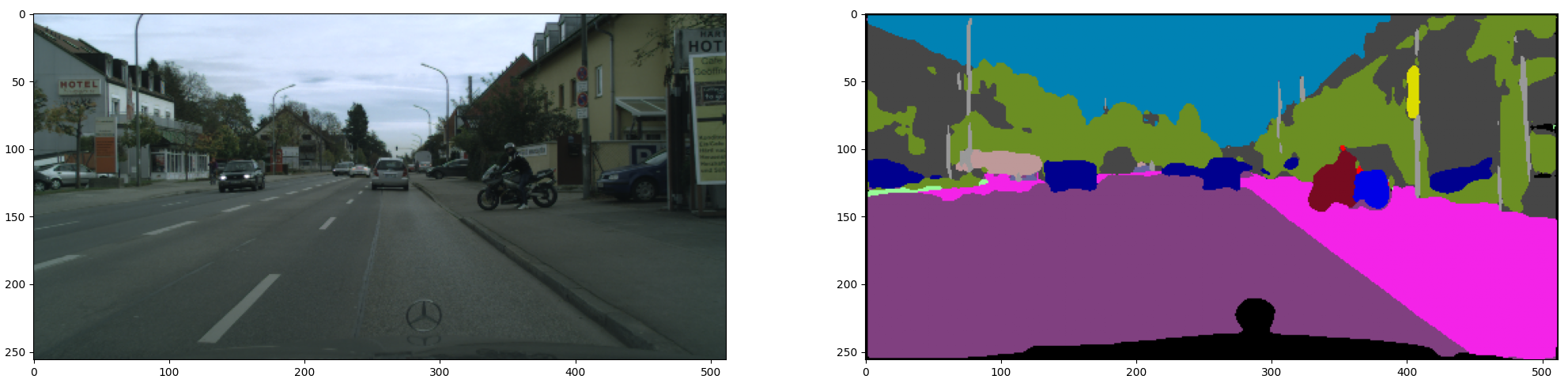
Part 02 : Inference on trained Semantic segmentation model
This briefly gives an overview of how a neural network could be used perform semantic segmentation inference. The previous post showed how a model could be trained and this builds upon that.
The training of the model is carried out by using models from segmentation_models_pytorch as this is an easy to use library for training several models. The training script is as follows
import cv2
import torch
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import utils_fn as util
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
use_opencv = False
imgPath = "path/to/the/image.png"
if use_opencv:
imgCV2 = cv2.imread(imgPath)
imgCV2 = cv2.cvtColor(imgCV2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img_tensor = util.transform(image=imgCV2)["image"].unsqueeze(0)
else:
imgPIL = Image.open(imgPath).convert("RGB")
img_tensor = util.transform(image=np.array(imgPIL))["image"].unsqueeze(0)
model = torch.load("chk_pts/trained_cityscapes_final.pth")["model"]
model.to(util.device)
model.eval()
# Get prediction:
with torch.no_grad():
prediction = model(img_tensor.to(util.device)).squeeze(0)
invimg = util.inv_normalize(img_tensor).squeeze(0)
output = prediction.detach().cpu()
t = torch.argmax(output, 0)
decoded_output = util.decode_segmap(t)
if use_opencv:
tt = cv2.cvtColor(decoded_output.astype(np.float32), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
numpy_horizontal = np.hstack((np.moveaxis(invimg.numpy(), 0, 2), tt))
cv2.namedWindow("image", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.imshow('image', numpy_horizontal)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
else:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(16, 50), facecolor='white')
ax[0].imshow(np.moveaxis(invimg.numpy(), 0, 2))
ax[1].imshow(decoded_output)
plt.show()
print("done")
Results